Author: Domingo H.C
Published on: December 10, 2025
Introduction
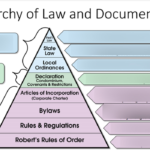
The Kelsen Pyramid, also known as the Hierarchy of Legal Norms, is one of the most important concepts in modern legal theory. Developed by Austrian jurist Hans Kelsen, the pyramid explains how laws are structured from the highest level of authority to the lowest.
Understanding the Kelsen Pyramid is essential for students, lawyers, public officials, and anyone studying how legal systems maintain order, coherence, and legitimacy.
What Is the Kelsen Pyramid?
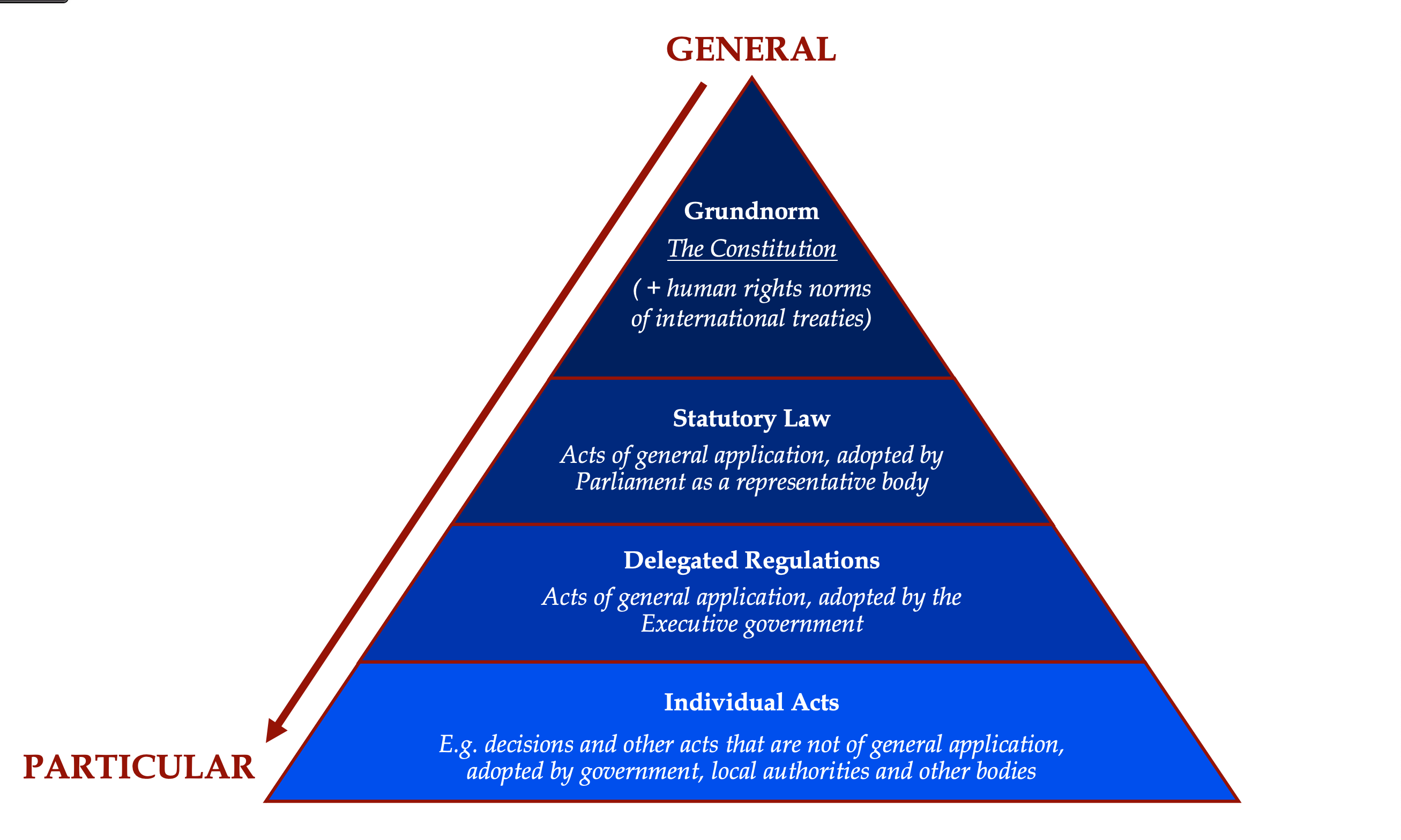
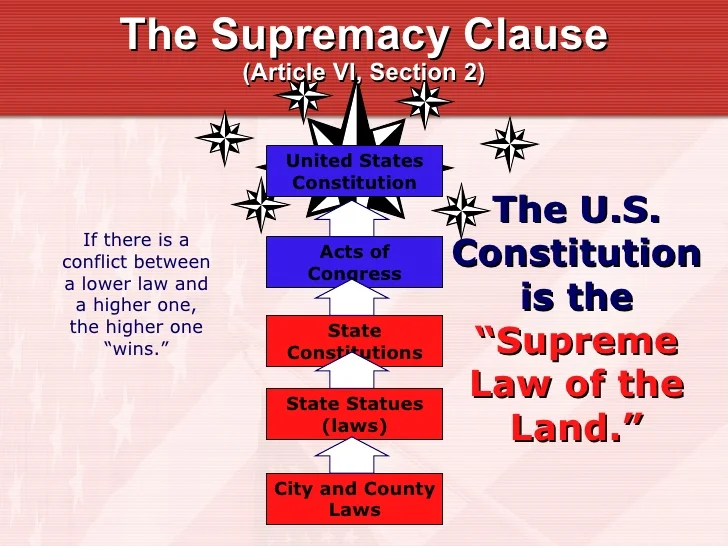
The Kelsen Pyramid is a visual representation of the hierarchy of legal norms within a legal system. It shows that not all laws have the same power and that each law depends on a higher norm for its validity.
At the top of the pyramid is the Constitution, the supreme legal norm. Below it are laws, regulations, administrative rules, and individual legal acts.
The Structure of the Kelsen Pyramid
Hans Kelsen divided the hierarchy of norms into several layers:
1. Constitution (Supreme Norm)
The Constitution is the highest legal norm.
Everything—laws, regulations, judgments—must comply with it.
Characteristics:
-
Defines rights, duties, and government structure
-
Highest authority
-
Invalidates any law that contradicts it
2. Ordinary Laws (Legislative Norms)
These laws are created by the legislative branch and must follow the Constitution.
Examples:
-
Civil Codes
-
Penal Codes
-
Labor Laws
3. Regulations (Administrative Norms)
Issued by the executive branch, ministries, or administrative agencies.
Purpose:
-
Detail how laws are applied
-
Provide procedures and mechanisms
4. Individual Legal Acts (Specific Decisions)
These include:
-
Court rulings
-
Contracts
-
Administrative resolutions
They are valid only if they follow all higher norms.
Why the Kelsen Pyramid Matters
The pyramid is essential because it ensures:
-
Legal order
-
Consistency and coherence
-
Predictability
-
Constitutional supremacy
-
Protection of citizens’ rights
Without a hierarchy, the legal system would collapse into contradiction and confusion.
Constitutional Supremacy in the Kelsen Pyramid
A key idea in Kelsen’s theory is the supremacy of the Constitution, meaning:
-
All laws must comply with it
-
Courts can invalidate unconstitutional laws
-
Governments cannot act beyond constitutional limits
This principle protects democracy, rights, and the separation of powers.
The Role of the Constitutional Court
In most countries, the Constitutional Court or Supreme Court ensures that all norms respect the Constitution.
These courts can:
-
Strike down unconstitutional laws
-
Interpret the Constitution
-
Protect fundamental rights
This judicial oversight is essential for maintaining the hierarchy of norms.
How the Kelsen Pyramid Prevents Legal Conflicts
If two laws contradict each other, the system uses the pyramid to decide which prevails:
-
A law overrides a regulation
-
The Constitution overrides any law
-
Lower norms must follow higher ones
This prevents arbitrary power and ensures equality before the law.
Criticisms of the Kelsen Pyramid
Although influential, some scholars criticize the model because:
-
It assumes that law flows only from top to bottom
-
Modern societies sometimes blur the boundaries
-
International law challenges strict hierarchy
-
Some countries use complex hybrid systems
However, the pyramid remains fundamental in legal education.
Real-World Examples of the Kelsen Pyramid
Examples from different countries:
United States
-
Constitution (Supreme Law)
-
Federal laws
-
State laws
-
Local regulations
Spain
-
Constitution
-
Organic laws
-
Ordinary laws
-
Royal decrees
Mexico
-
Constitution
-
Federal laws
-
State laws
-
Municipal regulations
All follow Kelsen’s hierarchical logic.
Conclusion
The Kelsen Pyramid remains one of the most influential concepts in legal theory. By organizing norms from the Constitution down to administrative rules, it ensures stability, justice, and consistency in the legal system.
Understanding this hierarchy allows citizens and professionals to interpret the law correctly and defend their rights effectively.
Final Call to Action
👉 Want more legal theory explained in simple language?
Explore more educational articles at Haroon E-Store and stay informed with high-quality legal content.